
| glossary | menu | Normal | lg | hc | 8.) Rosgen Classification of Stability and Change > Debris & Channel Obstruction Influences |
| < Previous | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | Next > |
Debris & Channel Obstruction Influences
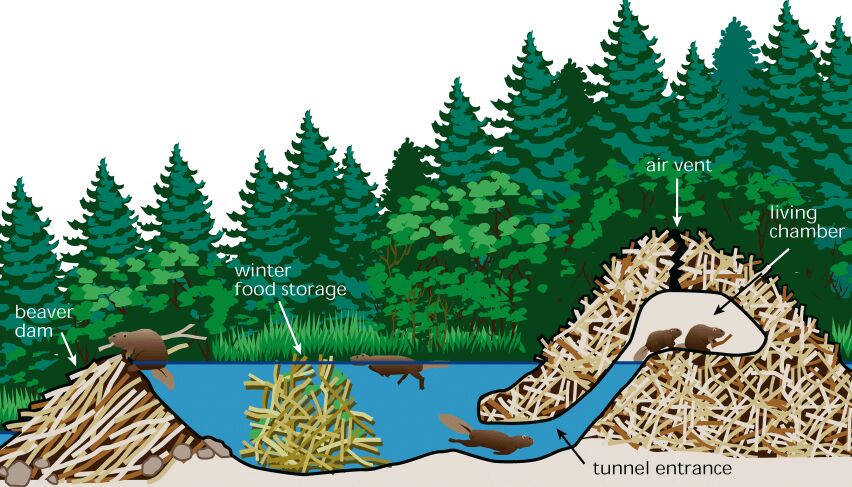
Debris directly influences channel stability and pattern, profile and dimension evolution. Debris blockages include:
- None
- Infrequent
- Moderate
- Extensive
- Dominating
- Beaver Dams - Few
- Beaver Dams - Frequent
- Beaver Dams - Abandoned
- Human Influences
Flood forecasting can use information about blockages and debris to anticipate FGM and flood response. Rosgen reports that a reduction in woody debris, for example, in a headwater A, B, or G channel often results in increased Erosion and loss of the step/pool spacing, often at 4 to 5 Bankfull Widths in 2% slope channels or 1.5 to 2 Bankfull Widths in 6% slope channels.
Image courtesy of FISRWG
| < Previous | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | Next > |