
| glossary | menu | Normal | lg | hc | 8.) Rosgen Classification of Stability and Change > Flow Regime Influences |
| < Previous | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | Next > |
Flow Regime Influences
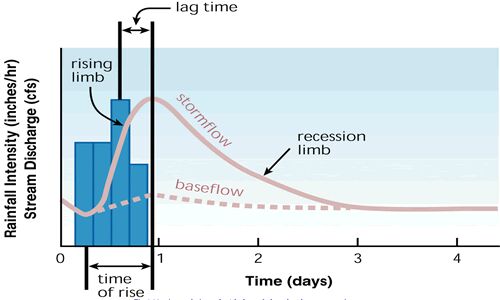
Channel flow exerts a strong influence on channel morphology. Flow regimes to distinguish include:
- Ephemeral
- Intermittent
- Perennial
- Subterranean
Flow regime patterns include: snowmelt, storm flow, glacial melt, spring fed, ice-flows, tidal influence, and regulated channel flow.
Channel classification types are used to compare probable response to channel flow regimes. Further, channel Bankfull Discharges that extend beyond the ranges of predicted from regional relationship curves are frequently the result of flow regime adjustment, including natural factors such as Karst losses.
Operational forecasters regularly monitor perennial rivers, however many headwater triggered floods arise due to ephemeral or intermittent flows, as well as snowmelt and ice-flow conditions.
Image courtesy of FISRWG
| < Previous | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | Next > |