
| glossary | menu | Normal | lg | hc | 4.) Geomorphologic Classification Systems > M-B Source to Sink Scheme |
| < Previous | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | Next > |
M-B Source to Sink Scheme
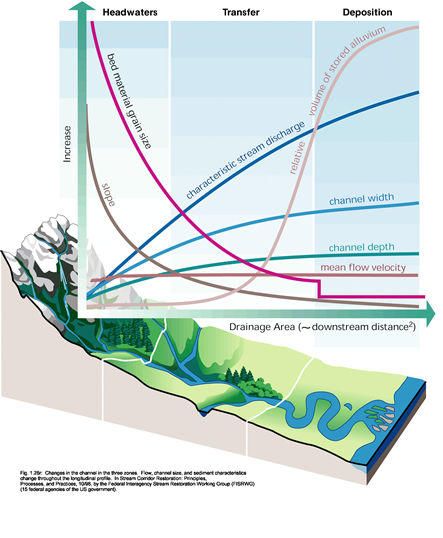
Montgomery-Buffington classification can characterize headwater, transfer, and Deposition channels. Typically, headwater and transfer channels serve the function of sediment delivery between steep sloped Colluvial sediment sources and higher order Deposition channel sinks.
Headwater channels are characterized as having steeper slopes and greater sized bed material, with relatively low volumes of stored Alluvium. Colluvial type channels might be in this category. Transfer channels have increasing width, depth, and discharge, with lower slopes and smaller bed material sizes. Deposition channel have much greater relative volumes of storage for transported Alluvium, and increased width, depth, and discharge associated with higher order Streams.
Image courtesy of FISRWG
| < Previous | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | Next > |